Introduction
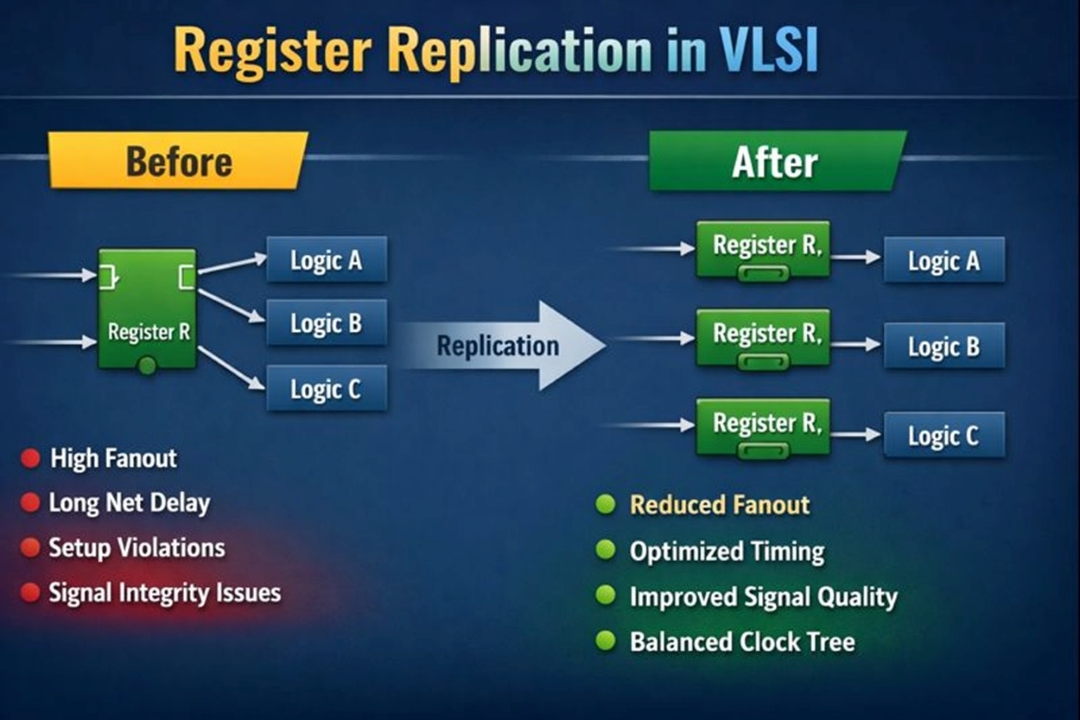
Register Replication is an optimization technique used in VLSI design where a single register driving many loads (high fanout) is duplicated into multiple identical registers. Each replicated register drives a smaller set of loads.
The functionality of the design remains unchanged, but timing and signal integrity are significantly improved.
How Register Replication Works
Register replication works by replacing one high-fanout register with multiple identical registers, each driving a smaller portion of the logic, while maintaining the same functionality.
To resolve this, the tool creates multiple replicas of the original register. All replicated registers share the same clock, input data, and control logic, ensuring functional equivalence.
The original fanout loads are then distributed among the replicated registers so that each register drives fewer loads. This significantly reduces net capacitance and interconnect delay, leading to improved timing performance.
Each replicated register is placed close to its respective loads, which reduces interconnect (net) delay and optimizes overall timing performance.
Importance of Register Replication
Register replication plays a crucial role in modern VLSI design by addressing timing and fanout-related issues.
- Reduces high fanout on registers
- Lowers net capacitance and interconnect delay
- Improves setup timing and slack
- Enhances clock tree balance
- Helps achieve timing closure in high-performance designs
Impact of Register Replication
Register replication has a direct impact on several key design metrics in VLSI.
- It improves timing performance by reducing fanout, net delay, and signal transition time, which helps eliminate setup timing violations.
- It leads to an increase in area, as additional registers are introduced into the design.
- Power consumption may also increase slightly due to the added clocked elements and clock tree loading.
- Register replication improves placement and routing quality, as registers are placed closer to their loads, reducing routing congestion and wire length.
- It enhances clock tree balance, resulting in reduced clock skew and more predictable clock behavior.
Conclusion
Overall, register replication provides a net positive impact on timing closure, especially in high-performance and advanced-node designs, with a manageable trade-off in area and power.